Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yin, Y.-G.*; Mori, Yoshinao*; Suzui, Nobuo*; Kurita, Keisuke; Yamaguchi, Mitsutaka*; Miyoshi, Yuta*; Nagao, Yuto*; Ashikari, Motoyuki*; Nagai, Keisuke*; Kawachi, Naoki*
New Phytologist, 232(5), p.1974 - 1984, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:65.39(Plant Sciences)Rice (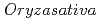 ) plants have porous or hollow organs consisting of aerenchyma, which is presumed to function as a low-resistance diffusion pathway for air to travel from the foliage above the water to submerged organs. However, gas movement in rice plants has yet to be visualized in real time. In this study involving partially submerged rice plants, the leaves emerging from the water were fed nitrogen-13-labeled nitrogen ([
) plants have porous or hollow organs consisting of aerenchyma, which is presumed to function as a low-resistance diffusion pathway for air to travel from the foliage above the water to submerged organs. However, gas movement in rice plants has yet to be visualized in real time. In this study involving partially submerged rice plants, the leaves emerging from the water were fed nitrogen-13-labeled nitrogen ([ N]N
N]N ) tracer gas, and the gas movement downward along the leaf blade, leaf sheath, and internode over time was monitored.
) tracer gas, and the gas movement downward along the leaf blade, leaf sheath, and internode over time was monitored.
 C-imaging revealed the spatiotemporal variability in the translocation of photosynthates into strawberry fruits in response to increasing daylight integrals at leaf surface
C-imaging revealed the spatiotemporal variability in the translocation of photosynthates into strawberry fruits in response to increasing daylight integrals at leaf surfaceMiyoshi, Yuta*; Hidaka, Kota*; Yin, Y.-G.*; Suzui, Nobuo*; Kurita, Keisuke; Kawachi, Naoki*
Frontiers in Plant Science (Internet), 12, p.688887_1 - 688887_14, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:76.93(Plant Sciences)In this study,  C-photosynthate translocation into strawberry fruits in individual plants was visualized non-invasively and repeatedly using a positron emission tracer imaging system (PETIS) to assess the spatiotemporal variability in the translocation dynamics in response to increasing daylight integrals. This is the first study to use
C-photosynthate translocation into strawberry fruits in individual plants was visualized non-invasively and repeatedly using a positron emission tracer imaging system (PETIS) to assess the spatiotemporal variability in the translocation dynamics in response to increasing daylight integrals. This is the first study to use  C-radioisotopes to clarify the spatiotemporal variability in photosynthate translocation from source leaves to individual sink fruits in vivo in response to increasing daylight integrals at a high spatiotemporal resolution.
C-radioisotopes to clarify the spatiotemporal variability in photosynthate translocation from source leaves to individual sink fruits in vivo in response to increasing daylight integrals at a high spatiotemporal resolution.
Yin, Y.-G.*; Suzui, Nobuo*; Kurita, Keisuke; Miyoshi, Yuta*; Unno, Yusuke*; Fujimaki, Shu*; Nakamura, Takuji*; Shinano, Takuro*; Kawachi, Naoki*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 10, p.8446_1 - 8446_11, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:59.51(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The release of rhizodeposits differs depending on the root position and is closely related to the assimilated carbon (C) supply. Therefore, quantifying the C partitioning over a short period may provide crucial information for clarifying root-soil carbon metabolism. A non-invasive method for visualising the translocation of recently assimilated C into the root system inside the rhizobox was established using  CO
CO labelling and the positron-emitting tracer imaging system. The spatial distribution of recent
labelling and the positron-emitting tracer imaging system. The spatial distribution of recent  C-photoassimilates translocated and released in the root system and soil were visualised for white lupin (
C-photoassimilates translocated and released in the root system and soil were visualised for white lupin (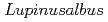 ) and soybean (
) and soybean (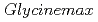 ). Our method enabled the quantification of the spatial C allocations in roots and soil, which may help to elucidate the relationship between C metabolism and nutrient cycling at specific locations of the root-soil system in response to environmental conditions over relatively short periods.
). Our method enabled the quantification of the spatial C allocations in roots and soil, which may help to elucidate the relationship between C metabolism and nutrient cycling at specific locations of the root-soil system in response to environmental conditions over relatively short periods.
 N]N
N]N gas for visualization of nitrogen fixation and translocation in nodulated soybean
gas for visualization of nitrogen fixation and translocation in nodulated soybeanYin, Y.-G.*; Ishii, Satomi*; Suzui, Nobuo*; Igura, Masato*; Kurita, Keisuke; Miyoshi, Yuta*; Nagasawa, Naotsugu*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa*; Kawachi, Naoki*
Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 151, p.7 - 12, 2019/09
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:55.67(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Accurate analysis of N fixation in leguminous crops requires determination of N utilization within an intact plant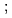 however, most approaches require tissue disassembly. We developed a simple and rapid technique to generate high-purity and high-yield [
however, most approaches require tissue disassembly. We developed a simple and rapid technique to generate high-purity and high-yield [ N]N
N]N gas and obtained real-time images of N fixation in an intact soybean plant. The purification efficiency was
gas and obtained real-time images of N fixation in an intact soybean plant. The purification efficiency was  81.6% after decay correction.
81.6% after decay correction.
 C]CO
C]CO
Matsuhashi, Shimpei; Fujimaki, Shu; Uchida, Hiroshi*; Ishioka, Noriko; Kume, Tamikazu
Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 64(4), p.435 - 440, 2006/04
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:77.5(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Matsuhashi, Shimpei; Suzui, Nobuo; Ishioka, Noriko
JAERI-Conf 2005-010, 79 Pages, 2005/09
no abstracts in English
Arakawa, Kazuo
Hoshasen Kagaku, (80), p.57 - 59, 2005/09
no abstracts in English
Matsuhashi, Shimpei; Fujimaki, Shu; Kawachi, Naoki; Sakamoto, Koichi; Ishioka, Noriko; Kume, Tamikazu
Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 51(3), p.417 - 423, 2005/06
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:52.22(Plant Sciences)no abstracts in English
Fateh, B.; Ishioka, Noriko; Watanabe, Satoshi; Kume, Tamikazu; Sekine, Toshiaki*
JAERI-Review 2003-033, TIARA Annual Report 2002, p.259 - 261, 2003/11
no abstracts in English
Matsuhashi, Shimpei
Isotope News, (592), p.2 - 7, 2003/08
no abstracts in English
Keutgen, N.; Matsuhashi, Shimpei; Mizuniwa, Chizuko; Ito, Takehito*; Fujimura, Takashi; Ishioka, Noriko; Watanabe, Satoshi; Sekine, Toshiaki; Uchida, Hiroshi*; Hashimoto, Shoji
Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 57(2), p.225 - 233, 2002/09
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:54.86(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)no abstracts in English
 C]methionine translocation in barley in relation to mugineic acid phytosiderophore biosynthesis
C]methionine translocation in barley in relation to mugineic acid phytosiderophore biosynthesisBughio, N.*; Nakanishi, Hiromi*; Kiyomiya, Shoichiro*; Matsuhashi, Shimpei; Ishioka, Noriko; Watanabe, Satoshi; Uchida, Hiroshi*; Tsuji, Atsunori*; Osa, Akihiko; Kume, Tamikazu; et al.
Planta, 213(5), p.708 - 715, 2001/09
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:36.85(Plant Sciences)[ C]Methionine ([
C]Methionine ([ C]Met) was supplied through barley roots and the
C]Met) was supplied through barley roots and the  C signal was follwoed using a real-time imaging system (PETIS), with subsequent development of autoradiographic images of the whole plant. In all cases, [
C signal was follwoed using a real-time imaging system (PETIS), with subsequent development of autoradiographic images of the whole plant. In all cases, [ C]Met was first translocated to the discrimination center, and this part was strongly labeled. Met absorbed by roots of the plants was subsequently translocated to other parts of the plant. In Fe-deficient (-Fe) barley plants, a drastic reduction in [
C]Met was first translocated to the discrimination center, and this part was strongly labeled. Met absorbed by roots of the plants was subsequently translocated to other parts of the plant. In Fe-deficient (-Fe) barley plants, a drastic reduction in [ C]Met translocation from the roots to the shoot was observed, while a greater amount of
C]Met translocation from the roots to the shoot was observed, while a greater amount of  C was found in the leaves of Fe-sufficient or Met-pretreated -Fe plants. Treatment of -Fe plants with amiooxyacetic acid increased the translocation of [
C was found in the leaves of Fe-sufficient or Met-pretreated -Fe plants. Treatment of -Fe plants with amiooxyacetic acid increased the translocation of [ C]Met to the shoot. The retention of exogenously supplied [
C]Met to the shoot. The retention of exogenously supplied [ C]Met in the roots of -Fe barley indicates that the Met is used in the biosynthesis of mugineic acid (MA) in barley roots. This and the absence of Met movement from shoots to the roots suggest that the MA phytosiderophores precursor Met originates in the roots of plants.
C]Met in the roots of -Fe barley indicates that the Met is used in the biosynthesis of mugineic acid (MA) in barley roots. This and the absence of Met movement from shoots to the roots suggest that the MA phytosiderophores precursor Met originates in the roots of plants.
 F-labeled water movement in a cowpea plant by positron emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS)
F-labeled water movement in a cowpea plant by positron emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS)Furukawa, Jun*; Yokota, Harumi*; Tanoi, Keitaro*; Ueoka, Shiori*; Matsuhashi, Shimpei; Ishioka, Noriko; Watanabe, Satoshi; Uchida, Hiroshi*; Tsuji, Atsunori*; Ito, Takehito*; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 249(2), p.495 - 498, 2001/08
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:73.21(Chemistry, Analytical)We present real time Vanadate (V ) uptake imaging in a cowpea plant by Positron Emitting Tracer Imaging System (PETIS). Vanadium-48 was produced by bombarding a Sc foil target with 50 MeV
) uptake imaging in a cowpea plant by Positron Emitting Tracer Imaging System (PETIS). Vanadium-48 was produced by bombarding a Sc foil target with 50 MeV  -particles at Takasaki Ion accelerators for Advanced Radiation Application (TIARA) AVF cyclotron. Then
-particles at Takasaki Ion accelerators for Advanced Radiation Application (TIARA) AVF cyclotron. Then  V was added to the culture solution to investigate the V distribution in a cowpea plant. The real time uptake of the
V was added to the culture solution to investigate the V distribution in a cowpea plant. The real time uptake of the  V was monitored by PETIS. We measured the distribution of
V was monitored by PETIS. We measured the distribution of  V in a whole plant after 3, 6 and 20 hours of V treatment by Bio-imaging Analyzer System (BAS). After the 20 hour treatment, vanadate was detected at the up-ground part of the plant. To know the effect of V uptake on plant activity,
V in a whole plant after 3, 6 and 20 hours of V treatment by Bio-imaging Analyzer System (BAS). After the 20 hour treatment, vanadate was detected at the up-ground part of the plant. To know the effect of V uptake on plant activity,  F-labeled water uptake was analyzed by PETIS. When a cowpea plant was treated with V for 20 hours before
F-labeled water uptake was analyzed by PETIS. When a cowpea plant was treated with V for 20 hours before  F-labeled water uptake experiment, the total amount of
F-labeled water uptake experiment, the total amount of  F-labeled water absorption was drastically desreased. Results suggest the inhibition of water uptake was mainly caused by the vanadate already moved to the up-ground part of the plant.
F-labeled water absorption was drastically desreased. Results suggest the inhibition of water uptake was mainly caused by the vanadate already moved to the up-ground part of the plant.
 F used as tracer to study water uptake and transport imaging of a cowpea plant
F used as tracer to study water uptake and transport imaging of a cowpea plantNakanishi, Tomoko*; Tanoi, Keitaro*; Yokota, Harumi*; Kang, D.-J.*; Ishii, Ryuichi*; Ishioka, Noriko; Watanabe, Satoshi; Osa, Akihiko; Sekine, Toshiaki; Matsuhashi, Shimpei; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 249(2), p.503 - 507, 2001/08
We present the water uptake ability of cowpea (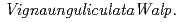 ) which has been regarded as one of the most drought resistant species among the pulse crops. It has been suggested that in the lower part of the stem, parenchymatous tissue for storing water had been developed for the function of deought resistance. We confirmed that in this tissue, water amount was high compared to the other stems by neutron radiography. Then the water uptake manner was measured by positron emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS) using
) which has been regarded as one of the most drought resistant species among the pulse crops. It has been suggested that in the lower part of the stem, parenchymatous tissue for storing water had been developed for the function of deought resistance. We confirmed that in this tissue, water amount was high compared to the other stems by neutron radiography. Then the water uptake manner was measured by positron emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS) using  F labeled water produced by a cyclotron. Comparing the water uptake manner of cowpea plant with that of common bean, cowpea plant was found to maintain high water uptake activity after drying treatment, suggesting the high drought resistant character.
F labeled water produced by a cyclotron. Comparing the water uptake manner of cowpea plant with that of common bean, cowpea plant was found to maintain high water uptake activity after drying treatment, suggesting the high drought resistant character.
Chino, Mitsuo*; Kume, Tamikazu
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 41(10), p.35 - 36, 1999/10
no abstracts in English
Kume, Tamikazu
Radioisotopes, 48(1), p.37 - 47, 1999/00
no abstracts in English
Kume, Tamikazu
Hoshasen To Sangyo, (80), p.4 - 5, 1998/00
no abstracts in English
Kume, Tamikazu; Fujimura, Takashi; Ishioka, Noriko; Uchida, Hiroshi*; Tsuji, Atsunori*
Nature, 389(6649), 1 Pages, 1997/09
no abstracts in English
 using
using  CO
CO and a positron-emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS)
and a positron-emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS)Fujimaki, Shu; Koyanagi, Atsushi*; Kawachi, Naoki; Suzui, Nobuo; Yin, Y.-G.; Ishii, Satomi; Shimada, Hiroaki*
no journal, ,
We developed an experimental system to evaluate photosynthetic activities of  individuals using
individuals using  CO
CO tracer gas and a positron-emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS). Two petri dishes each containing nine Arabidopsis plants (16 days or 20 days after sown) were placed into an airtight cabinet, and approximately 40 MBq of
tracer gas and a positron-emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS). Two petri dishes each containing nine Arabidopsis plants (16 days or 20 days after sown) were placed into an airtight cabinet, and approximately 40 MBq of  CO
CO was introduced with normal air. The gas in the cabinet was flushed out after 10 minutes of contact, then the dishes were mounted on the center of field of view of the imaging system, and the dynamic image of carbon distribution in the plants was acquired for 1 hour. As a result, the rates of carbon fixation and of carbon translocation in the respective individuals were estimated through quantitative analysis of the image data. Furthermore, the source and sink strength were visualized as a pixel-by-pixel map. Our method is valuable for quantitative analysis of effects of specific genes or substances on photoassimilation and partitioning.
was introduced with normal air. The gas in the cabinet was flushed out after 10 minutes of contact, then the dishes were mounted on the center of field of view of the imaging system, and the dynamic image of carbon distribution in the plants was acquired for 1 hour. As a result, the rates of carbon fixation and of carbon translocation in the respective individuals were estimated through quantitative analysis of the image data. Furthermore, the source and sink strength were visualized as a pixel-by-pixel map. Our method is valuable for quantitative analysis of effects of specific genes or substances on photoassimilation and partitioning.